Technologies Used
Project Gallery
Description
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, make sure you have the following prerequisites:
- Kubernetes cluster up and running.
kubectlcommand-line tool installed and configured to access your Kubernetes cluster.- Basic knowledge of Kubernetes concepts and YAML configuration files.
Step 1: create a namespace
To get started, create a namespace inside k8s Cluster, to do that you can simply run the following command:
kubectl create ns demo-elastic
Step 2: create persistent volume For Data-elastic
- Create a file called
elasticsearch-pvc.ymland add the following YAML configuration:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-pvc
labels:
component: elasticsearch
spec:
# storageClassName: standard
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1G
---
2. Apply the configuration to deploy PVC:
kubectl apply -f elasticsearch-pvc.yaml -n demo-elastic
Step 3: Deploy Elasticsearch
- Create a file called
elasticsearch-deployment.yamland add the following YAML configuration:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: elasticsearch
spec:
serviceName: elasticsearch
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
component: elasticsearch
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: elasticsearch
spec:
containers:
- name: elasticsearch
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.12.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: discovery.type
value: single-node
ports:
- containerPort: 9200
name: http
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- name: elasticsearch-config
mountPath: /usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml
subPath: elasticsearch.yml
- name: elasticsearch-data
mountPath: /usr/share/elasticsearch/data
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 4Gi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 4Gi
# Allow non-root user to access PersistentVolume
securityContext:
fsGroup: 1000
restartPolicy: Always
volumes:
- name: elasticsearch-config
configMap:
name: elasticsearch-config
- name: elasticsearch-data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: elasticsearch-pvc
1.2 Apply the configuration to deploy Elasticsearch:
kubectl apply -f elasticsearch-deployment.yaml -n demo-elastic
1.3 Create a file called elasticsearch-service.yaml and add the following YAML configuration:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: elasticsearch
labels:
component: elasticsearch
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
component: elasticsearch
ports:
- port: 9200
targetPort: 9200
1.4 Apply the configuration to service Elasticsearch:
kubectl apply -f elasticsearch-service.yaml -n demo-elastic
1.5 Create a file called elasticsearch-configmap.yaml and add the following YAML configuration:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-config
labels:
component: elasticsearch
data:
elasticsearch.yml: |
cluster.name: Demo-Elastic
node.name: Master
path.data: /usr/share/elasticsearch/data
http:
host: 0.0.0.0
port: 9200
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
transport.host: 127.0.0.1
xpack.license.self_generated.type: basic
# Enable xpack.security which is provided in basic subscription
xpack.security.enabled: true
# Disable unused xpack features
xpack.monitoring.enabled: false
xpack.graph.enabled: false
xpack.watcher.enabled: false
xpack.ml.enabled: false
With the following command, we can now set up passwords for built-in users and install Elasticsearch to our cluster. During kibana and fluentd configuration, we’ll employ “elastic” users.
Disclaimer: I recommend enhancing the use of credentials in your production deployment by using Secrets over Configmaps, using distinct users for Kibana, and becoming more familiar with the least access concept.
$ kubectl exec -it elasticsearch-0 -n demo-elastic -- bin/elasticsearch-setup-passwords auto -b ... ##Changed password for user elasticPASSWORD elastic = ismail-wajdi-7415b3176
- 6 Apply the configuration to config-Map Elasticsearch:
kubectl apply -f elasticsearch-configmap.yam -n demo-elastic
Step 4: Deploy Kibana
1.1 Create a file called elasticsearch-kibana.yaml and add the following YAML configuration:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: kibana
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
component: kibana
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: kibana
spec:
containers:
- name: kibana
image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.12.0
env:
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_URL
value: http://elasticsearch:9200
- name: XPACK_SECURITY_ENABLED
value: "true"
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: kibana-config
key: elasticsearch_username
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: kibana-config
key: elasticsearch_password
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: kibana-config
ports:
- containerPort: 5601
name: http
protocol: TCP
1.2 Apply the configuration to deploy Kibana:
kubectl apply -f elasticsearch-Kibana.yaml -n demo-elastic
1.3 Create a file called Kibana-service.yaml and add the following YAML configuration:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kibana
labels:
component: kibana
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
component: kibana
ports:
- port: 5601
targetPort: 5601
1.4 Apply the configuration to service Kibana:
kubectl apply -f Kibana-service.yaml -n demo-elastic
1.5 Create a file called Kibana-configmap.yaml and add the following YAML configuration:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kibana-config
labels:
component: kibana
data:
elasticsearch_username: elastic
elasticsearch_password: ismail-wajdi-7415b3176
1.6 Apply the configuration to config-Map Kibana:
kubectl apply -f Kibana-configmap.yaml -n demo-elastic
Step 5: Accessing Elasticsearch and Kibana
Before proceeding, make sure you have the following prerequisites:
1. Obtain the external IP addresses and Port of the Elasticsearch and Kibana services:
kubectl get svc -n NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE elasticsearch NodePort 10.233.39.51 <none> 9200:31012/TCP 6h12m kibana NodePort 10.233.5.197 <none> 5601:32398/TCP 6h4m
2. Once you have the external IP addresses, you can access Elasticsearch and Kibana using a web browser or tools like cURL or a REST client.
3. Accessing Elasticsearch: Open a web browser or use a tool like cURL and visit http://<elasticsearch-external-ip>:9200. If Elasticsearch is running successfully, you will see information about the Elasticsearch cluster, confirming that it is accessible.
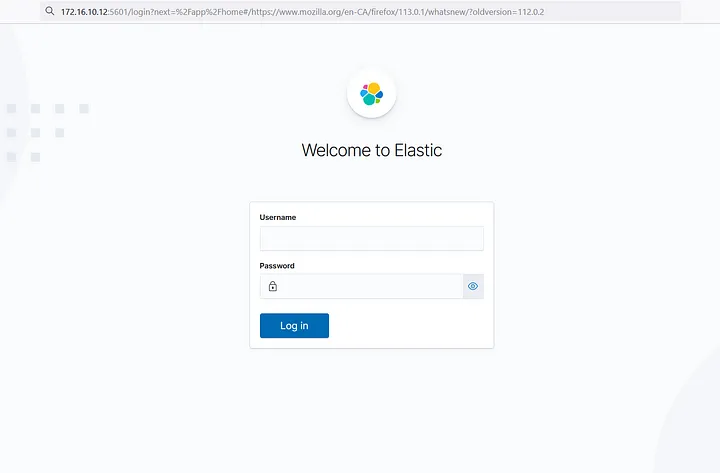
4. Accessing Kibana: Open a web browser and navigate to http://<kibana-external-ip>:5601. This will take you to the Kibana login page. Enter the elastic username and the password generated during the setup process. Once authenticated, you will have access to the Kibana dashboard, where you can explore and analyze data, create visualizations and dashboards, and perform various tasks provided by the Kibana interface.
By following these steps, you have successfully deployed Elasticsearch with a Kibana instance on Kubernetes, along with password protection. You can now access Elasticsearch to interact with the data and open Kibana to leverage its powerful features for data analysis and visualization. The external IP addresses obtained allow you to access Elasticsearch and Kibana securely from a web browser or through API calls, ensuring that only authorized users can access and utilize these services.